更新時間:2022-09-23 17:10:50 來源:動力節點 瀏覽1224次
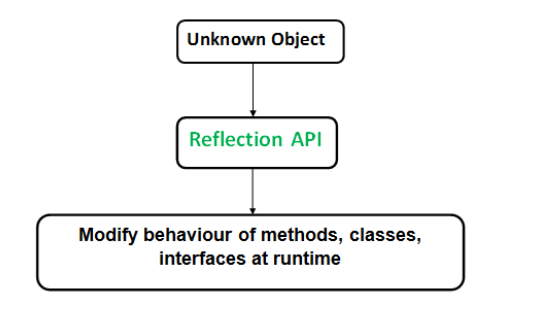
學習Java中的反射其實不難,反射是一種 API,用于在運行時檢查或修改方法、類和接口的行為。反射所需的類在java.lang.reflect包下提供,這對于理解反射至關重要。所以我們用視覺輔助來說明這個包,以便更好地理解如下:
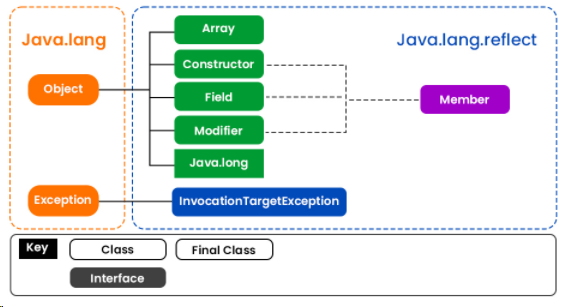
反射可用于獲取有關類、構造函數和方法的信息,如下表所示:
班級 getClass() 方法用于獲取對象所屬的類的名稱。
構造函數getConstructors() 方法用于獲取對象所屬類的公共構造函數。
方法getMethods() 方法用于獲取對象所屬類的公共方法。
如果我們知道它的名稱和參數類型,我們可以通過反射調用方法。為此,我們使用如下所述的兩種方法,然后繼續進行如下操作:
getDeclaredMethod()
調用()
方法一: getDeclaredMethod (): 創建要調用的方法的對象。
語法:此方法的語法
Class.getDeclaredMethod(名稱,參數類型)
參數:
方法二: invoke():它在運行時調用類的方法我們使用下面的方法。
句法:
Method.invoke(對象,參數)
提示:如果類的方法不接受任何參數,則將 null 作為參數傳遞。
注意:通過反射,我們可以借助類對象訪問類的私有變量和方法,并使用上面討論的對象調用方法。為此,我們使用以下兩種方法。
方法三: Class.getDeclaredField(FieldName):用于獲取私有字段。返回指定字段名稱的 Field 類型的對象。
方法 4: Field.setAccessible(true): 允許訪問該字段,而不考慮與該字段一起使用的訪問修飾符。
從反射 API 得出的重要觀察結果
可擴展性特性:應用程序可以通過使用它們的完全限定名稱創建可擴展性對象的實例來使用外部的、用戶定義的類。
調試和測試工具:調試器使用反射屬性來檢查類的私有成員。
性能開銷:反射操作的性能比非反射操作慢,在性能敏感的應用程序中頻繁調用的代碼部分應避免使用。
內部暴露:反射代碼破壞了抽象,因此可能會隨著平臺的升級而改變行為。
例子
// Java Program to demonstrate the Use of Reflection
// Importing required classes
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
// Class 1
// Of Whose object is to be created
class Test {
// creating a private field
private String s;
// Constructor of this class
// Constructor 1
// Public constructor
public Test() { s = "GeeksforGeeks"; }
// Constructor 2
// no arguments
public void method1()
{
System.out.println("The string is " + s);
}
// Constructor 3
// int as argument
public void method2(int n)
{
System.out.println("The number is " + n);
}
// Constructor 4
// Private method
private void method3()
{
System.out.println("Private method invoked");
}
}
// Class 2
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception
{
// Creating object whose property is to be checked
// Creating an object of class 1 inside main()
// method
Test obj = new Test();
// Creating class object from the object using
// getClass() method
Class cls = obj.getClass();
// Printing the name of class
// using getName() method
System.out.println("The name of class is "
+ cls.getName());
// Getting the constructor of the class through the
// object of the class
Constructor constructor = cls.getConstructor();
// Printing the name of constructor
// using getName() method
System.out.println("The name of constructor is "
+ constructor.getName());
// Display message only
System.out.println(
"The public methods of class are : ");
// Getting methods of the class through the object
// of the class by using getMethods
Method[] methods = cls.getMethods();
// Printing method names
for (Method method : methods)
System.out.println(method.getName());
// Creates object of desired method by
// providing the method name and parameter class as
// arguments to the getDeclaredMethod() method
Method methodcall1
= cls.getDeclaredMethod("method2", int.class);
// Invoking the method at runtime
methodcall1.invoke(obj, 19);
// Creates object of the desired field by
// providing the name of field as argument to the
// getDeclaredField() method
Field field = cls.getDeclaredField("s");
// Allows the object to access the field
// irrespective of the access specifier used with
// the field
field.setAccessible(true);
// Takes object and the new value to be assigned
// to the field as arguments
field.set(obj, "JAVA");
// Creates object of desired method by providing the
// method name as argument to the
// getDeclaredMethod()
Method methodcall2
= cls.getDeclaredMethod("method1");
// Invokes the method at runtime
methodcall2.invoke(obj);
// Creates object of the desired method by providing
// the name of method as argument to the
// getDeclaredMethod() method
Method methodcall3
= cls.getDeclaredMethod("method3");
// Allows the object to access the method
// irrespective of the access specifier used with
// the method
methodcall3.setAccessible(true);
// Invoking the method at runtime
methodcall3.invoke(obj);
}
}
輸出:
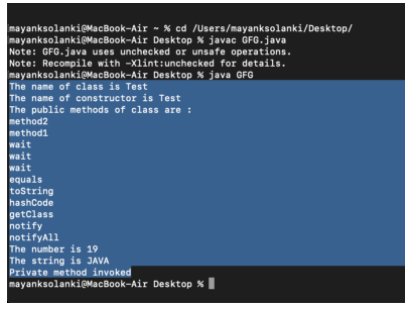
以上就是動力節點小編介紹的"Java反射學習,要點你抓好了嗎",希望對大家有幫助,如有疑問,請在線咨詢,有專業老師隨時為您務。
 Java實驗班
Java實驗班
0基礎 0學費 15天面授
 Java就業班
Java就業班
有基礎 直達就業
 Java夜校直播班
Java夜校直播班
業余時間 高薪轉行
 Java在職加薪班
Java在職加薪班
工作1~3年,加薪神器
 Java架構師班
Java架構師班
工作3~5年,晉升架構
提交申請后,顧問老師會電話與您溝通安排學習