更新時間:2019-08-30 10:56:50 來源:動力節點 瀏覽3583次
今天動力節點java培訓機構小編為大家介紹“JAVA中list.contains()方法,要重寫equals(),hashcode()方法”,希望能夠幫助正在學習java的零基礎學員,下面就隨小編一起看看吧。
object對象中的 public boolean equals(Object obj),對于任何非空引用值 x 和 y,當且僅當 x 和 y 引用同一個對象時,此方法才返回 true;
注意:當此方法被重寫時,通常有必要重寫 hashCode 方法,以維護 hashCode 方法的常規協定,該協定聲明相等對象必須具有相等的哈希碼。如下:
(1)當obj1.equals(obj2)為true時,obj1.hashCode() == obj2.hashCode()必須為true
(2)當obj1.hashCode() == obj2.hashCode()為false時,obj1.equals(obj2)必須為false
如果不重寫equals,那么比較的將是對象的引用是否指向同一塊內存地址,重寫之后目的是為了比較兩個對象的value值是否相等。特別指出利用equals比較八大包裝對象
(如int,float等)和String類(因為該類已重寫了equals和hashcode方法)對象時,默認比較的是值,在比較其它自定義對象時都是比較的引用地址
hashcode是用于散列數據的快速存取,如利用HashSet/HashMap/Hashtable類來存儲數據時,都是根據存儲對象的hashcode值來進行判斷是否相同的。
這樣如果我們對一個對象重寫了euqals,意思是只要對象的成員變量值都相等那么euqals就等于true,但不重寫hashcode,那么我們再new一個新的對象,
當原對象.equals(新對象)等于true時,兩者的hashcode卻是不一樣的,由此將產生了理解的不一致,如在存儲散列集合時(如Set類),將會存儲了兩個值一樣的對象,
導致混淆,因此,就也需要重寫hashcode()
舉例說明:
import java.util.*;
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
Collection c = new HashSet();
c.add("hello");
c.add(new Name("f1","l1"));
c.add(new Integer(100));
c.remove("hello");
c.remove(new Integer(100));
System.out.println(c.remove(new Name("f1","l1")));
*/
Name n1 = new Name("01");
Name n2 = new Name("01");
Collection c = new HashSet();
c.add(n1);
System.out.println("------------");
c.add(n2);
System.out.println("------------");
System.out.println(n1.equals(n2));
System.out.println("------------");
System.out.println(n1.hashCode());
System.out.println(n2.hashCode());
System.out.println(c);
}
}
class Name {
private String id;
public Name(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String toString(){
return this.id;
}
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (obj instanceof Name) {
Name name = (Name) obj;
System.out.println("equal"+ name.id);
return (id.equals(name.id));
}
return super.equals(obj);
}
public int hashCode() {
Name name = (Name) this;
System.out.println("Hash" + name.id);
return id.hashCode();
}
}
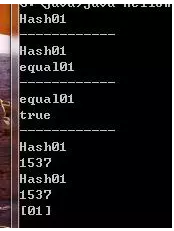
image.png
就這個程序進行分析,在第一次添加時,調用了hashcode()方法,將hashcode存入對象中,第二次也一樣,然后對hashcode進行比較。hashcode也只用于HashSet/HashMap/Hashtable類存儲數據,所以會用于比較,需要重寫
總結,自定義類要重寫equals方法來進行等值比較,自定義類要重寫compareTo方法來進行不同對象大小的比較,重寫hashcode方法為了將數據存入HashSet/HashMap/Hashtable類時進行比較。
以上就是動力節點java培訓機構介紹的“JAVA中list.contains()方法,要重寫equals(),hashcode()方法”的內容,希望能夠幫助到大家,更多精彩內容請繼續關注動力節點java培訓機構官網,每天會有精彩內容分享與你。
相關免費視頻教程推薦
List存儲自定義類型數據需要重寫equals方法(視頻教程下載):http://www.dabaquan.cn/xiazai/2487.html
 Java實驗班
Java實驗班
0基礎 0學費 15天面授
 Java就業班
Java就業班
有基礎 直達就業
 Java夜校直播班
Java夜校直播班
業余時間 高薪轉行
 Java在職加薪班
Java在職加薪班
工作1~3年,加薪神器
 Java架構師班
Java架構師班
工作3~5年,晉升架構
提交申請后,顧問老師會電話與您溝通安排學習