Java面向?qū)ο?/div>
- Java基礎(chǔ)教程
- Java包(package)
- Eclipse安裝教程
- Java訪問(wèn)權(quán)限
- Java Object類
- Java中final關(guān)鍵字的作用
- Java抽象類
- Java接口
- Java類與類之間的關(guān)系
- Java內(nèi)部類
Java異常
Java數(shù)組
- Java數(shù)組的定義
- Java訪問(wèn)數(shù)組元素
- Java數(shù)組元素的遍歷
- Java數(shù)組的靜態(tài)初始化
- Java數(shù)組引用數(shù)據(jù)類型
- Java可變長(zhǎng)參數(shù)
- Java數(shù)組擴(kuò)容
- Java數(shù)組的特點(diǎn)
- Java對(duì)象數(shù)組
- Java二維數(shù)組
- Java中arrays工具類
- Java數(shù)組算法
Java常用類
Java集合
- Java中Collection集合概述
- Java中Collection的基本操作
- Java中List集合
- Java中ArrayList與Vector的區(qū)別
- Java中LinkedList詳解
- Java Set集合與HashSet集合特點(diǎn)
- Java TreeSet集合
- Java Collection集合小結(jié)
- Java中Collections工具類
- Java泛型詳解
- Java中Map集合概述
- Java中Map基本操作
- Java HashMap底層實(shí)現(xiàn)原理
- HashTable和HashMap的區(qū)別
- Java Properties類
- Java TreeMap排序
- Java Map集合小結(jié)
Java IO流
- Java IO流的分類
- Java文件輸入輸出流
- Java緩沖輸入輸出流
- Java數(shù)據(jù)輸入輸出流
- Java打印流與Java裝飾者設(shè)計(jì)模式
- Java對(duì)象輸入輸出流
- Java文件字符輸入輸出流
- Java字符輸入輸出流
- Java緩沖字符輸入輸出流
- Java File類概述
- File類常用操作
Java線程
- Java線程概述
- Java創(chuàng)建線程的方式
- Java線程基礎(chǔ)操作
- Java線程的生命周期
- Java線程調(diào)度
- Java線程同步
- Java線程安全的類
- Java設(shè)計(jì)模式之生產(chǎn)者消費(fèi)者模式
- Java Timer定時(shí)器
- Java線程死鎖
Java反射
- Java反射概述
- Java反射類的信息
- Java反射字段信息
- Java反射方法
- Java反射構(gòu)造方法
- Java反射創(chuàng)建實(shí)例
- Java通過(guò)反射訪問(wèn)字段值
- Java通過(guò)反射調(diào)用方法
- Java Properties實(shí)例
Socket編程
Java注解開(kāi)發(fā)
- 什么是Java注解
- JDK自帶注解
- Java開(kāi)發(fā)自定義注解
- Java注解開(kāi)發(fā)實(shí)例:通過(guò)注解創(chuàng)建數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)表
Java GoF設(shè)計(jì)模式
HashMap
Java內(nèi)存模型
- Java內(nèi)存模型的概念
- Java并發(fā)編程
- Java內(nèi)存模型
- Java中Volatile關(guān)鍵字
- Java Volatile關(guān)鍵字使用場(chǎng)景
- JVM內(nèi)存模型
Java線性表
Java數(shù)組擴(kuò)容
當(dāng)數(shù)組定義完成后,數(shù)組存儲(chǔ)元素的個(gè)數(shù)就確定了,因?yàn)樵诙x數(shù)組時(shí),要指定數(shù)組的長(zhǎng)度. 如果想要在數(shù)組中存儲(chǔ)更多的數(shù)據(jù), 就需要對(duì)數(shù)組擴(kuò)容。
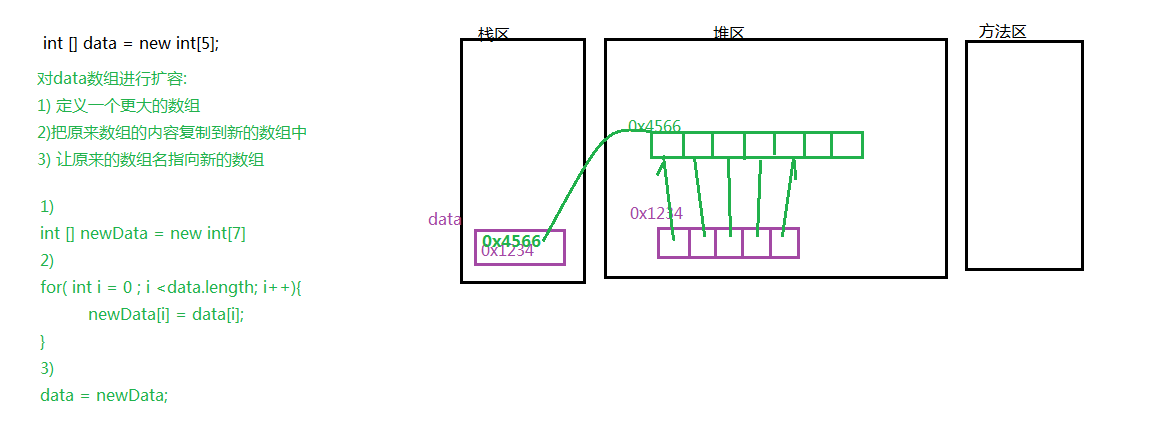
package com.wkcto.chapter03.demo01;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* 數(shù)組擴(kuò)容
* @author 蛙課網(wǎng)
*
*/
public class Test06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// m1(); //完全手動(dòng)擴(kuò)容
// m2(); //數(shù)組復(fù)制調(diào)用 了System.arraycopy(0方法
m3(); //調(diào)用 Arrays.copyOf(0實(shí)現(xiàn)擴(kuò)容
}
private static void m3() {
// 定義長(zhǎng)度為5的數(shù)組
int[] data = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
// 想要在數(shù)組中存儲(chǔ)更多的數(shù)據(jù),需要對(duì)數(shù)組擴(kuò)容
//Arrays工具類copyOf(源數(shù)組, 新數(shù)組的長(zhǎng)度) 可以實(shí)現(xiàn)數(shù)組的擴(kuò)容
data = Arrays.copyOf(data, data.length*3/2);
System.out.println( Arrays.toString(data));
}
private static void m2() {
//定義長(zhǎng)度為5的數(shù)組
int [] data = {1,2,3,4,5};
//想要在數(shù)組中存儲(chǔ)更多的數(shù)據(jù),需要對(duì)數(shù)組擴(kuò)容
//(1) 定義一個(gè)更大的數(shù)組
int [] newData = new int[data.length * 3 / 2] ; //按1.5倍大小擴(kuò)容
//(2)把原來(lái)數(shù)組的內(nèi)容復(fù)制到新數(shù)組中
//把src數(shù)組從srcPos開(kāi)始的length個(gè)元素復(fù)制到dest數(shù)組的destPos開(kāi)始的位置
// System.arraycopy(src, srcPos, dest, destPos, length);
System.arraycopy(data, 0, newData, 0, data.length);
//arraycopy()方法使用了native修飾,沒(méi)有方法體, 該方法的方法體可能是由C/C++實(shí)現(xiàn)的
//JNI,Java native Interface技術(shù),可以在Java語(yǔ)言中調(diào)用其他語(yǔ)言編寫的代碼
//(3) 讓原來(lái)的數(shù)組名指向新的數(shù)組
data = newData;
//
System.out.println( Arrays.toString(data));
}
private static void m1() {
//1)定義長(zhǎng)度為5的數(shù)組
int [] data = {1,2,3,4,5};
//2)想要在數(shù)組中存儲(chǔ)更多的數(shù)據(jù),需要對(duì)數(shù)組擴(kuò)容
//(1) 定義一個(gè)更大的數(shù)組
int [] newData = new int[data.length * 3 / 2] ; //按1.5倍大小擴(kuò)容
//(2)把原來(lái)數(shù)組的內(nèi)容復(fù)制到新數(shù)組中
for( int i = 0 ; i < data.length; i++){
newData[i] = data[i];
}
//(3) 讓原來(lái)的數(shù)組名指向新的數(shù)組
data = newData;
//
System.out.println( Arrays.toString(data));
}
}






